FLANGES
WHAT IS FLANGES?
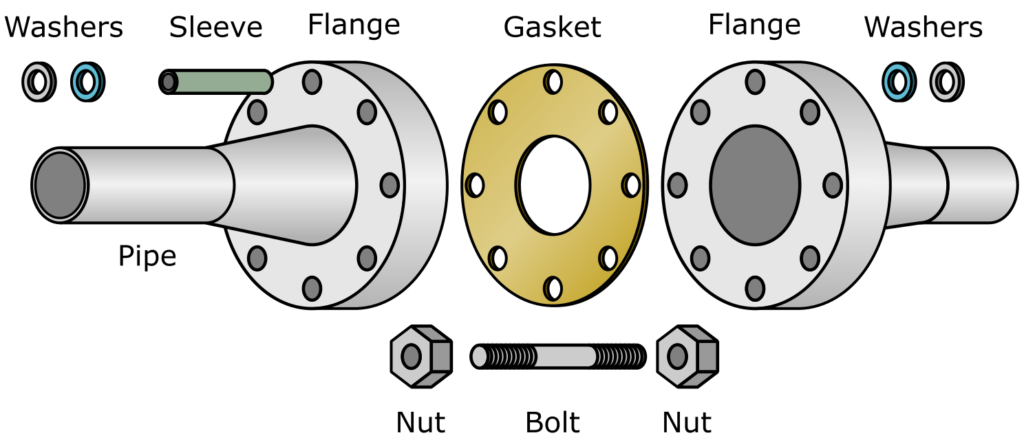
Flanges are external rims, edges, ribs, or collars used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment to form a piping system. They are typically circular and come with holes that allow them to be bolted together. Flanges are often used to facilitate easy assembly and disassembly of piping systems, and they can also be used for inspection, modification, or cleaning purposes.
FOR FLANGE TYPES
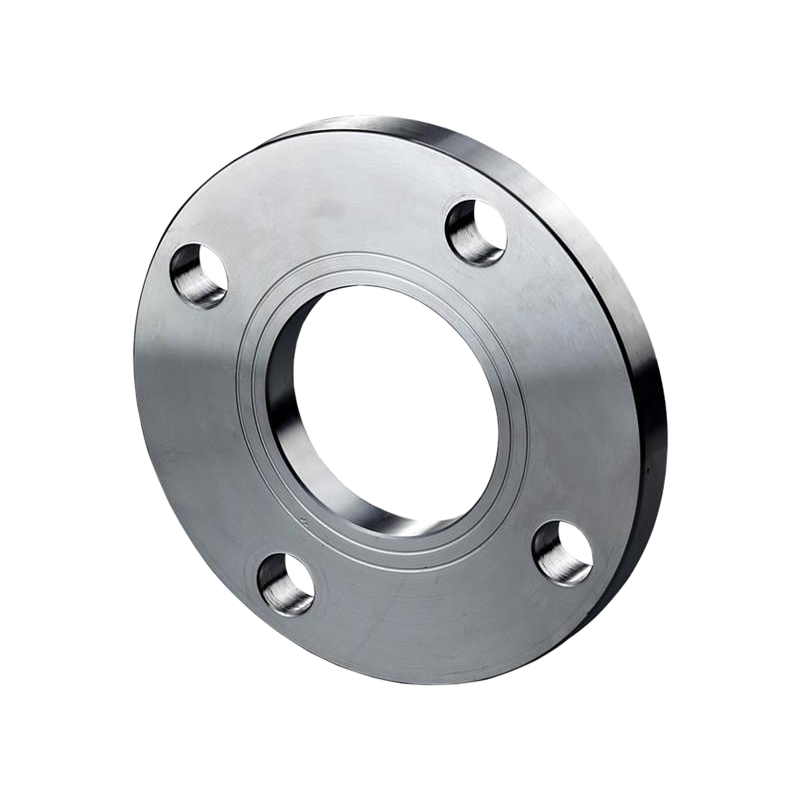

plate flange(PL)
This type is a flat, circular disk that is welded onto the end of a pipe and connects to another flange or fitting. Unlike more complex types of flanges, it doesn't have a raised face or a lip for a gasket. Plate flanges are generally used in less demanding applications where ease of assembly and cost are more important than high pressure and temperature resistance.
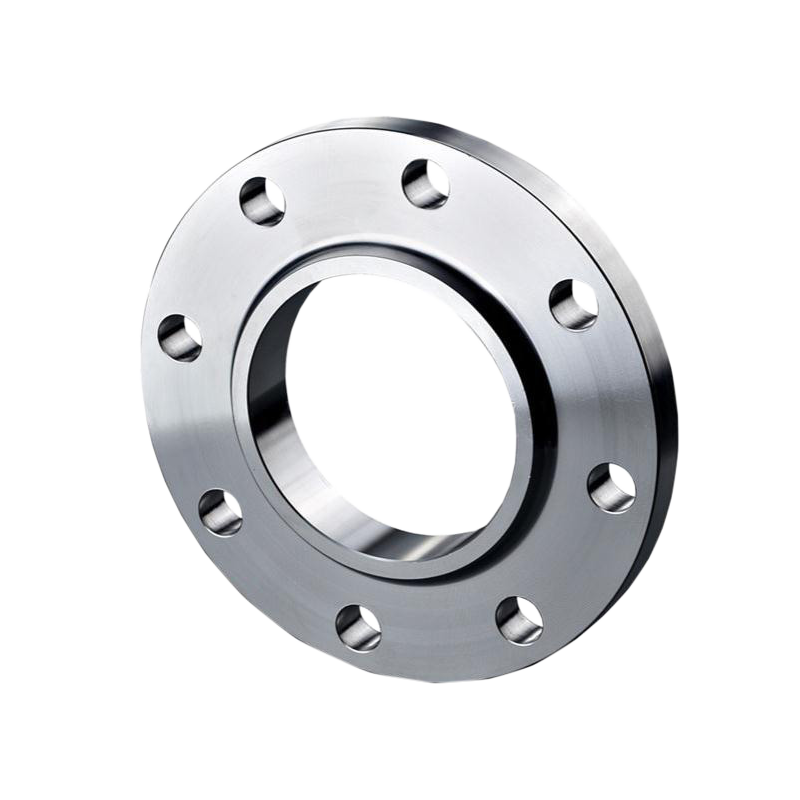

Slip-On Flanges(SO)
SO type are designed to slide over the end of a pipe and are then welded in place. They are easier and more economical to install compared to more robust types like weld neck flanges. Typically used in lower-pressure applications, slip-on flanges are popular in industries like water treatment and petrochemicals. They offer a convenient but less durable alternative for connecting pipes in a system.
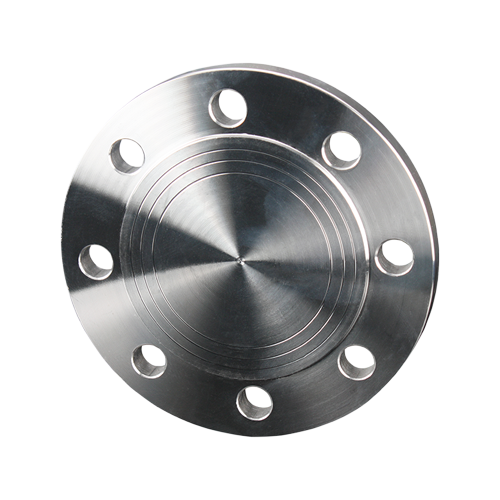

Blind Flanges(BL)
BL type is used to seal off a section of pipe or a nozzle on a vessel that is not in use. Unlike other flanges that are used to connect pipes, a blind flange is flat and does not have a bore, or hole, in the center. This design effectively blocks off the flow of fluid through a pipeline, allowing for maintenance, inspection, or system modifications.
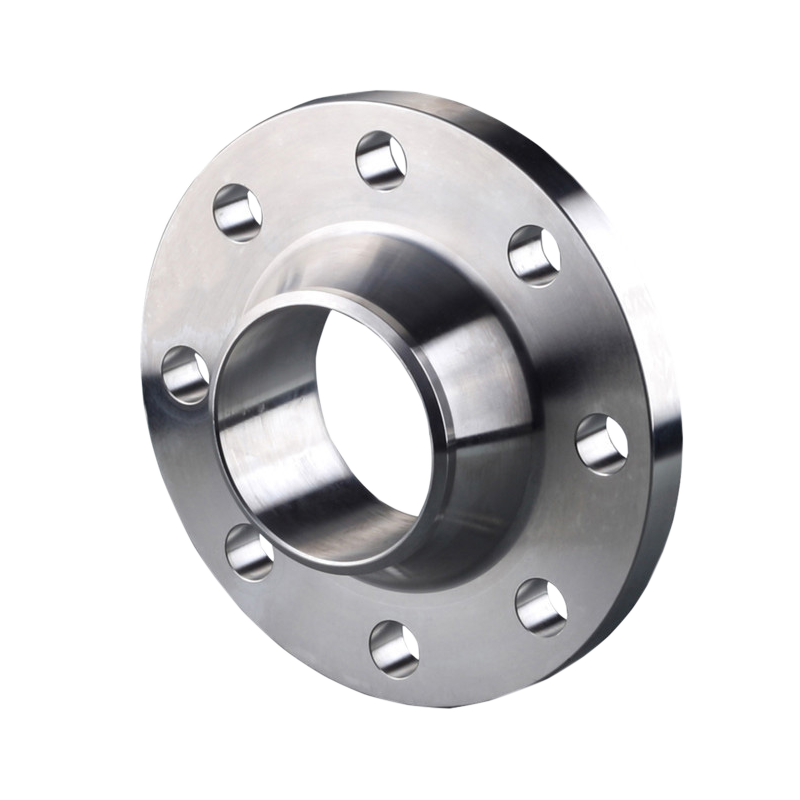

Weld Neck Flanges(wn)
WN type are a type of flange that is designed to be joined to a piping system by butt welding. Unlike other flanges that can be attached to the pipe in various ways, a weld neck flange has a long tapered hub that goes over the end of the pipe. This tapered hub provides an ideal welding area and offers a tight, high-integrity seal that prevents leaks and ensures durability under high stress.
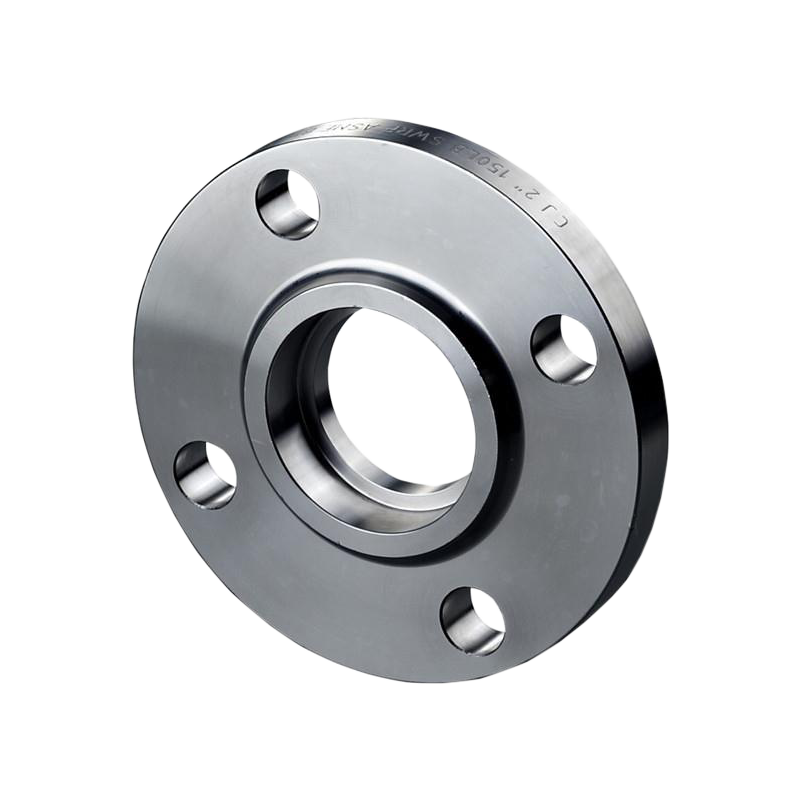

Socket Weld Flanges(SW)
SW type are used in applications requiring a strong but easily disassemblable connection. These flanges feature a socket into which the pipe is inserted and then fillet-welded to secure it in place. The design allows for a smooth bore and better fluid or gas flow inside the piping system. Socket weld flanges are often used in small-diameter, high-pressure applications such as hydraulic and steam lines.
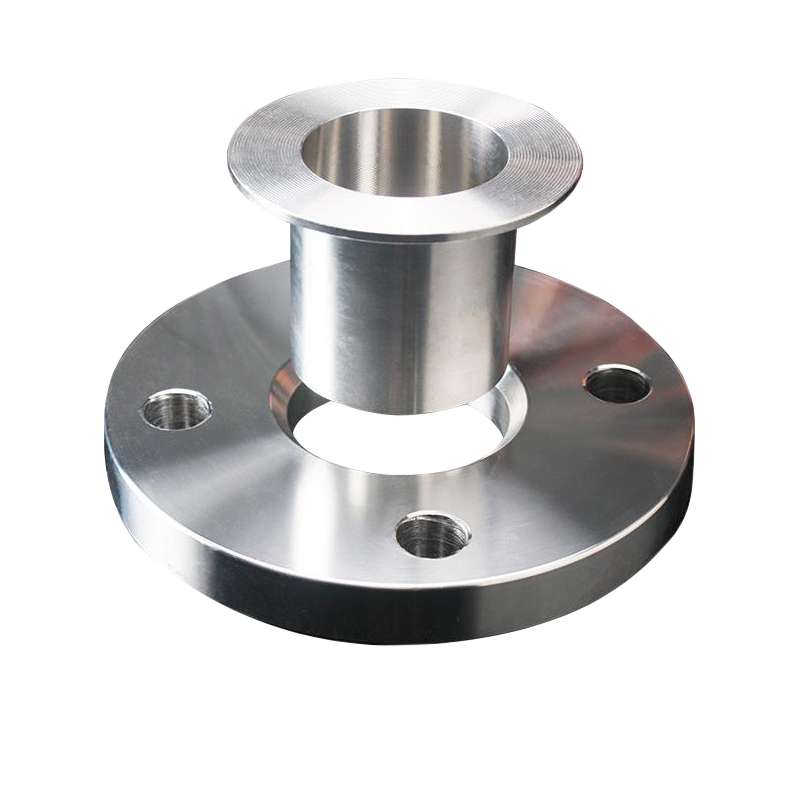

Loose Flange(Lap joint flange)
A Loose Flange, also known as a Lap Joint Flange, consists of a stub end welded to the pipe and a backing flange that slides over it. This design allows for easy maintenance and is often used in low-pressure applications where bolt-hole alignment or frequent system access is required. The flanges can be made from materials like carbon steel or stainless steel, depending on the application.
FOR FLANGE FACES
“flange faces” refers to the sealing area of a flange, where a gasket is usually placed to ensure a leak-proof connection between two flanges. The design of the flange face is critical to achieving an effective seal and varies depending on the application’s requirements for pressure, temperature, and chemical compatibility. Here are brief explanations of the examples you mentioned:
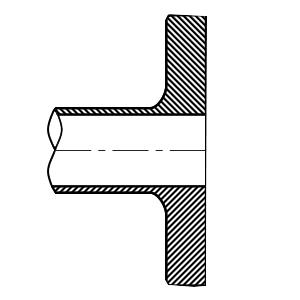
Flat face
A flat surface without any elevation, used mainly for low-pressure and non-critical applications.
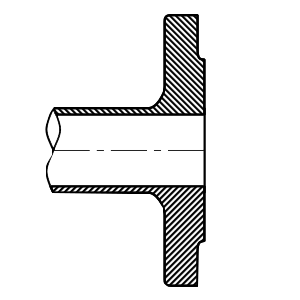
Raised Face
Features a raised area around the bore, common in many high-pressure applications and allows for a variety of gasket types.
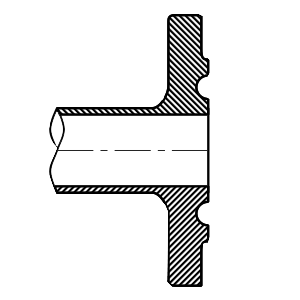
Ring-Type Joint (RTJ)
Features a grooved face that holds a metal ring gasket, used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
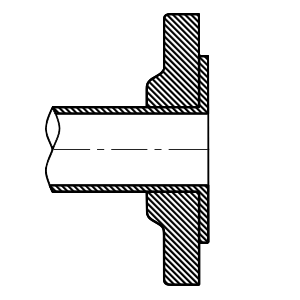
Lap Joint
Often used with a matching stub end, this face allows for easy alignment and is used primarily in systems that require frequent maintenance.
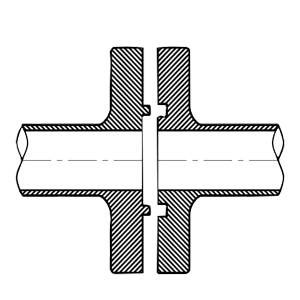
Tongue and Groove
One flange has a raised ring (tongue), and the other has a depressed ring (groove); they fit into each other to form a tight seal.
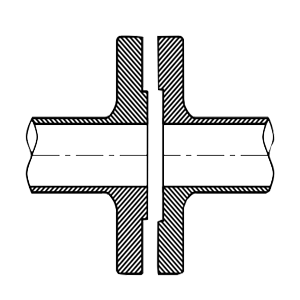
Male and Female
Similar to tongue and groove but more exaggerated; the male flange has an additional lip, and the female flange has a corresponding recess.
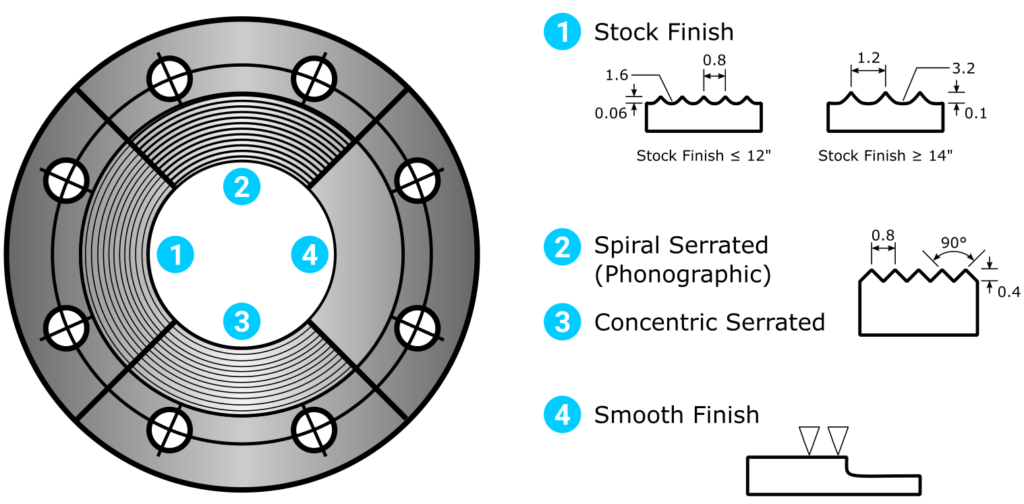
FOR FLANGE SURFACE FACES
the condition of the flange face sealing surface, often referred to as “flange surfaces,” is crucial for achieving a proper seal in a flanged connection. These surfaces may be smooth or serrated, and each type has its own applications and requirements.
Smooth Surface:(4) Generally used for soft gaskets or in low-pressure applications. The quality of the surface finish is often defined by its Roughness Average (Ra) or Arithmetic Average Roughness Height (AARH). These metrics quantify how smooth or rough the surface is on a microscopic level and are crucial for ensuring a leak-proof seal.
Serrated Surface(1,2,3): Also known as a “phonographic” finish, a serrated surface has concentric grooves cut into it. This type of finish is commonly used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications and is suitable for metal gaskets like ring-type joint (RTJ) gaskets.
HOW BALL VALVE WORK?
Flanges work by providing a mechanical method to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in a piping system. Here’s a simplified explanation of how flanges function:
- Selection: Choose the appropriate type and size of flanges based on the application, material compatibility, pressure ratings, and other relevant factors.
Installation: The flange is either slid over the pipe (as in slip-on flanges) or welded to it (as in weld neck flanges). In some cases, it may be screwed on (threaded flanges) or socket-welded.
Alignment: The flanges are aligned so that their bolt holes match, facilitating the insertion of bolts or studs.
Sealing: A gasket is placed between the two mating flange faces. This gasket serves as a seal to prevent leaks once the flanges are bolted together.
5. Bolting: Bolts or studs and nuts are used to securely fasten the two flanges together. The bolts are tightened in a crisscross pattern to apply even pressure on the gasket, ensuring a tight seal.
6.Testing: After installation, the joint is often tested under operating conditions to confirm the integrity of the seal and to ensure there are no leaks.
Flanges allow for easy assembly and disassembly of components, making them ideal for systems that require frequent maintenance, changes, or inspections. Different types of flanges and their accompanying surface finishes are chosen based on the specific requirements of the application, such as pressure and temperature conditions, as well as the type of fluid being transported.
MAIN STANDARDS WELFLOW PRODUCE
- ANSI/ASME B16.5 150LB
- ANSI/ASME B16.5 300LB
- ANSI/ASME B16.5 400LB
- ANSI/ASME B16.5 600LB
- ANSI/ASME B16.5 900LB
- EN1092-1 PN10/63
- EN1759-1 150LB/600LB
- BS4504 PN10/PN63
- JIS B2220 5K/63K
- ISO7005-1
- DIN2502/DIN2503
- DIN2573/DIN2576
- DIN 86029/DIN 86030
- DIN2633/DIN2635
- DIN 2566/DIN 2567/DIN2568
- GOST12820/12821/12836
- SABS 1123
- AS2129
- UNI2282/2283/2284
- UNI2277/2278
HELP YOU SELECT THE RIGHT flanges
Send us a message if you have any questions about ball valves. Our experts will give you a reply with 24 hours to help you select the right valve you want.
Tel: +86-577-88893652
Email: [email protected]
